Theory 1
Consider some process schematically with components in series and components in parallel:
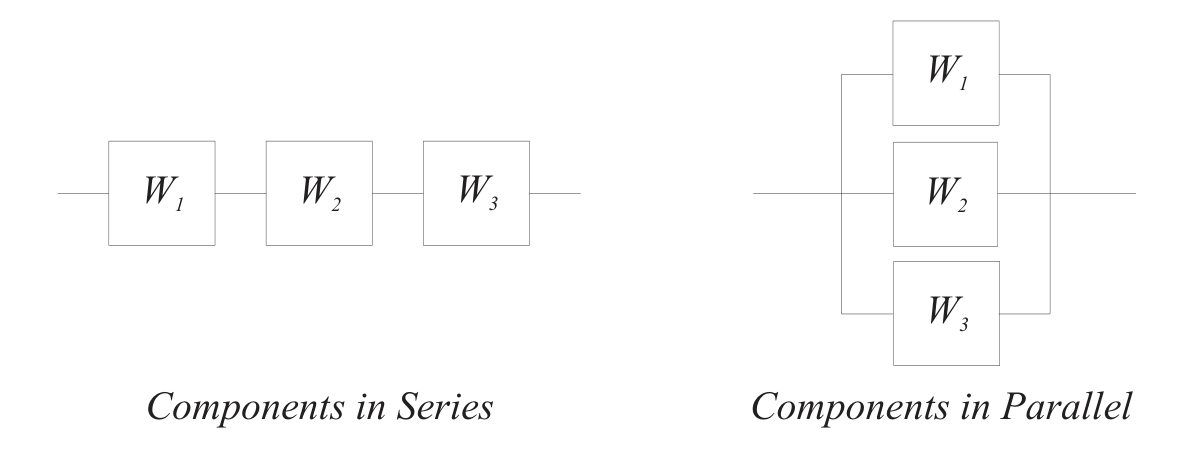
- Each component has a probability of success or failure.
- Event
indicates ‘success’ of that component (same name). - Then
is the probability of succeeding.
Success for a series of components requires success of each member.
- Series components rely on each other.
- Success of the whole is success of part 1 AND success of part 2 AND part 3, etc.
Failure for parallel components requires failure of each member.
- Parallel components represent redundancy.
- Success of the whole is success of part 1 OR success of part 2 OR part 3, etc.
For series components, stack successes:
For parallel components, stack failures:
E.g. if
- Series components:
- Parallel components:
To analyze a complex diagram of series and parallel components, bundle each:
- pure series set as a single compound component with its own success probability (the product)
- pure parallel set as a single compound component with its own success probability (using the failure formula)
This is like the analysis of resistors and inductors.