Stepwise problems - Thu. 11:59pm
Positive series
01
01
Integral Test (IT)
Use the Integral Test to determine whether the series converges:
Show your work. You must check that the test is applicable.
Link to originalSolution
01
First note that:
is continuous is positive is monotone decreasing because is increasing Then:
Since this is finite, the integral test establishes that the series converges.
Link to original
Series
02
03
Geometric series
Compute the following summation values using the sum formula for geometric series.
(a)
(b) Solution
02
(a)
First term:
Common ratio is
. Geometric series summation formula, always first term on top:
(b)
First term:
Common ratio:
Geometric series summation formula:
Link to original
Regular problems - Sun. 11:59pm
Sequences
03
06
Limits and convergence
For each sequence, either write the limit value (if it converges), or write ‘diverges’.
(a)
(b) (c) (d) (e)
(f) (g) (h) Solution
03
(a) diverges
(b) (c) diverges (d) (e)
(f) diverges:
(g)
(h)
Use L’Hopital’s Rule:
Link to original
04
07
Limits and convergence
For each sequence, either write the limit value (if it converges), or write ‘diverges’.
(a)
(b) (c) (d) (e)
(f) (g) Solution
04
(a)
(b) diverges:
(Note that
.)
(c)
: L’Hopital’s Rule:
(d)
by (c), the sign doesn’t affect convergence to
(e)
: Multiply above and below by
:
(f)
: This is a well-known formula for
. If that formula is not used as the definition of , then it would not be circular reasoning to argue as follows:
(g) diverges:
So:
Link to original
Series
05
04
Repeating digits
Using the geometric series formula, find the fractional forms of these decimal numbers:
(a)
(b) Solution
05
(a)
First term:
. Common ratio:
Geometric series summation formula:
(b)
This is geometric starting with
. First term:
. Common ratio:
. Geometric series summation formula:
Add back the first term:
Link to original
06
07
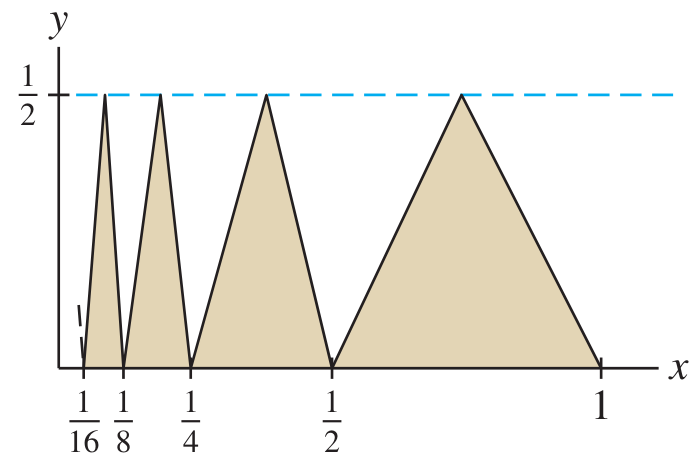
Total area of infinitely many triangles
Find the area of all the triangles as in the figure:
(The first triangle from the right starts at
, and going left they never end.) Solution
06
Compute the first few areas, with
being the area of the largest triangle: This is a geometric series with
: Geometric series total sum formula:
Link to original
07
02
Geometric series
Compute the following summation values using the sum formula for geometric series.
(a)
(b) Solution
07
(a)
The first term is
. The common ratio is . Therefore the sum:
(b)
Split numerator and obtain two geometric series:
Geometric series total sum formula:
Link to original
Positive series
08
04
Integral Test (IT)
Determine whether the series is convergent by using the Integral Test.
Show your work. You must check that the test is applicable.
(a)
(b) (c) Solution
08
(a) Verify applicability of the integral test:
is continuous for all . (Only discontinuity is at , but the series starts at .) since for all . is monotone decreasing, since as increases, the denominator increases, and the term decreases. Apply the integral test:
This is finite and the improper integral converges, so the series converges by the Integral Test.
(b) Verify applicability of the integral test with
:
is definitely continuous for all . since and for all . - Decreasing?
has zeros at . - When
, . - Series starts at
, so the terms are monotone decreasing. Apply the integral test:
This is finite and the improper integral converges, so the series converges by the Integral Test.
(c) Verify applicability of the integral test for
:
is continuous for all . (The only discontinuity is at , but the series starts at .) since for all . is monotone decreasing, since as increases, the denominator increases, and the term decreases. Apply the integral test:
This is finite and the improper integral converges, so the series converges by the Integral Test.
Link to original